This page contains 74 color-coded prepositional phrases used in example sentences. Each color-coded example sentence is accompanied by two or three methods of analysis. Each method of analysis illustrates a different way of thinking about how prepositional phrases function in a sentence.
Here is a list of all the simple prepositions (one-word prepositions) used in the example sentences. Be sure to take a look at the two pages devoted to complex-prepositions (multi-word prepositions).
1) aboard, 2) about, 3) above, 4) across, 5) after, 6) against, 7) along, 8) alongside, 9) amid, 10) amidst, 11) among, 12) amongst, 13) around, 14) as, 15) at, 16) atop, 17) before, 18) behind, 19) below, 20) beneath, 21) beside, 22) besides, 23) between, 24) beyond, 25) but (except), 26) by, 27) circa, 28) considering, 29) despite, 30) down, 31) during, 32) except, 33) excluding, 34) following, 35) for, 36) from, 37) given, 38) in, 39) including, 40) inside, 41) into, 42) like, 43) minus, 44) near, 45) notwithstanding, 46) of, 47) off, 48) on, 49) onto, 50) opposite, 51) outside, 52) over, 53) past, 54) pending, 55) per, 56) regarding, 57) sans, 58) since, 59) than, 60) through, 61) throughout, 62) to, 63) toward/towards, 64) under, 65) underneath, 66) unlike, 67) until, 68) up, 69) upon, 70) versus, 71) via, 72) with, 73) within, 74) without.
1. What are Complex Prepositions?
2. 82 Color-Coded Complex Prepositions in Prepositional Phrases – Example Sentences with Analysis
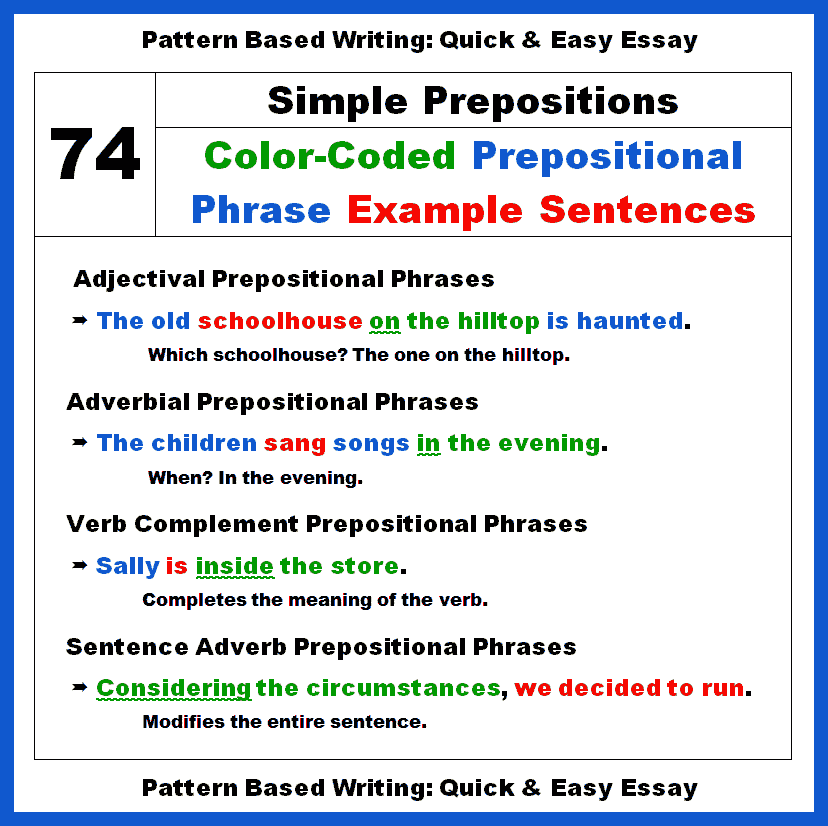
Color-Coded Key
• Green = The Entire Prepositional Phrase
• Green Italics with Underline = The Preposition
• Green Bold = The Object of the Preposition
• Red = The Word or Words that the Prepositional Phrase Modifies
• Adj. = Adjectival
• Adv. = Adverbial
Let’s Take a Look! Prepositional Phrase Examples and Analysis
1. aboard: Jim jumped aboard the trolley.
- Verb Complement – TEST: WHAT did Jim jump ABOARD? The trolley.
- Location » Change of Location » Goal: To what location?
- DO-SO TEST: Jim jumped aboard the trolley, and Jan did so aboard the bus. FAILED!
2. about: This book about horses is finely illustrated.
- Adj. – WHAT KIND of book? Book about horses.
3. above: The migrating geese flew above our heads.
- Adv. – WHERE did the migrating geese fly? Above our heads.
- Location » In what location or position?
4. across: The Viking explorers sailed across the ocean to a new world.
- Adv. – WHERE did Viking explorers sail? Across the ocean.
- Location » Change of Location » Path: Along what path?
5. after: The fire came after the earthquake.
- Adv. – WHEN did the fire come? After the earthquake.
- Time » Relative Position in Time: Came after what?
6. against: Jim placed the ladder against the wall.
- Adv. – WHERE did Jim place the ladder? Against the wall.
- Location » In what location or position?
7. along: Huck walked along the shore.
- Adv. – WHERE did Huck walk? Along the shore.
- Location » Change of Location » Path: Along what path?
8. alongside: The dolphins swam alongside our boat for almost an hour.
- Adv. – WHERE did the dolphins swim? Alongside our boat.
- Location » Change of Location – Path: Along what path?
9. amid: Together we strolled amid the blooming cherry blossoms.
- Adv. – WHERE did we stroll? Amid cherry blossoms.
- Location: In what location? (Note: in the middle of or surrounded by.)
10. amidst: The bees and ladybugs celebrated spring amidst the fragrant flowers.
- Adv. – WHERE did bees and ladybugs celebrate spring? Amidst the blooming flowers.
- Location: In what location? (Note: in the middle of or surrounded by.)
11. among: Only one person among us disagrees with our decision.
- Adj. – WHICH people disagree? One person among us. (Uses location to specify or limit which one.)
12. amongst: A traitor lurked amongst the troops.
- Adv. – WHERE did the traitor lurk? Amongst the troops.
- Location: In what location? (Note: in the middle of or between)
13. around: The large house around the corner is for sale.
- Adj. – WHICH house is for sale? The house around the corner. (Uses location to specify which one.)
14. as: I tell you this as a friend.
- Adv. – HOW do you tell me? As a friend.
- Process: How? In what way or in what manner?
15. at: Sam threw the dodge ball at me.
- Adv. – WHERE did Sam throw the dodge ball? At me.
- Location » Change of Location » Direction: In what direction?
16. atop: The old bell rested silently atop the old church.
- Adv. – WHERE did the old bell rest? Atop the old church.
- Location: In what location?
17. before: We arrived before the others.
- Adv. – WHEN did we arrive? Before the others.
- Time » Relative Position in Time: Arrived before whom?
18. behind: The cat is hiding behind the couch.
- Adv. – WHERE is the cat hiding? Behind the couch.
- Location: In what location?
19. below: The apartment below ours is for rent.
- Adj. – WHICH apartment is for rent? The apartment below ours. (Uses location to specify which one.)
20. beneath: A mysterious world lies beneath the ocean surface.
- Adv. – WHERE does a mysterious world lie? Beneath the ocean surface.
- Location: In what location?
21. beside: Karen placed her pencil beside her notebook.
- Verb Complement – WHERE did Karen place her pencil? Beside her notebook.
- Location: In what location?
- TEST: Karen placed her pencil. = INCOMPLETE SENTENCE
22. besides: Everyone besides David came to the party.
- Adj. – WHICH ONES? (Exception – WHICH ONES didn’t?)
23. between: The wall between the two houses is tall.
- Adj. – WHICH wall is tall? The wall between the two houses. (Uses location to specify which one.)
24. beyond: The farm just beyond ours is a chicken farm.
- Adj. – WHICH ONE? WHICH farm is a chicken farm? The farm beyond ours. (Uses location to specify which one.)
25. but: The child ate everything but the peas.
- Adj. – WHICH ONES? (Exception)
26. by: Columbus came to America by boat.
- Adv. – HOW did Columbus come to America? By boat.
- Process » Means: How? By what means?
27. circa: The period circa 1760 brought about great change.
- Adj. – WHICH period brought about great change? The period circa 1760. (particularizes)
28. considering: Considering the car’s condition, a low price is to be expected.
- Adv. – DISJUNCT/CONJUNCT
- Related to REASON: WHY is a low price to be expected? The car’s condition.
29. despite: Despite the rain, the football game continued.
- Adv. – WHY? (Related to Reason: Not because of the rain; but despite the rain.)
- OR Adv. – DISJUNCT/ADJUNCT
30. down: The store is just down the road.
- Verb Complement: WHERE is the store? Down the road.
- Location: In what location?
- TEST: The store is. = INCOMPLETE SENTENCE
=======================
Do you teach beginning writers or struggling writers? Be sure to check out Pattern Based Writing: Quick & Easy Essay on the homepage!=======================
31. during: We played board games during the storm.
- Adv. – WHEN did we play games? During the storm.
- Time » Time Period: What time period?
32. except: Everyone except Mark came to the party.
- Adj. – WHICH ONES? (Exception)
33. excluding: Everything in the store is on sale, excluding the guitars.
- Adj. – WHICH ONES? (Exception)
34. following: Following the news, everyone cheered.
- Adv. – WHEN did everyone cheer? Following the news.
- Time » Relative Position in Time: Cheered following what?
35. for: Monica asked Debbie for help.
- Verb Complement: TEST: WHAT did Monica ask Debbie FOR? Help.
- DO-SO TEST: Monica asked Debbie for help, and Bill did so for money. FAILED!
36. from: The family returned from Italy.
- Adv. – WHERE did the family return from? From Italy.
- Location » Change of Location » Source: From what location?
37. given: Given the circumstances, the meeting went well.
- Adv. – DISJUNCT/CONJUNCT
38. in: The ice cream is in the freezer.
- Verb Complement: WHERE is the ice cream? In the freezer.
- Location: In what location?
- TEST: The ice cream is. = INCOMPLETE SENTENCE
39. including: All the students, including Mark, sat quietly.
- Adj. – WHICH ONES? (specifies/inclusion)
40. inside: The cat is sleeping inside the box.
- Adv. – WHERE is the cat sleeping? Inside the box.
- Location: In what location?
41. into: Steve jumped into the pool.
- Adv. – WHERE did Steve jump? Into the pool.
- Location » Change of Location » Goal: To what location?
42. like: People like Mary always win.
- Adj. – WHICH people always win? People like Mary. (specifies/narrows by using comparison)
43. minus: Revenue minus expenses equals net income.
- Adj. – WHICH revenue equals net income? Revenue minus expenses. (narrows)
44. near: Kim sat near the exit.
- Adv. – WHERE did Kim sit? Near the exit.
- Location: In what location?
45. notwithstanding: Notwithstanding the controversy, the fundraiser was successful.
- Adv. – CONCESSIVE ADJUNCT: Related to Reason: WHY? Not because of the controversy; but notwithstanding the controversy. Notwithstanding what circumstances? Notwithstanding the controversy.
- OR Adv. – DISJUNCT/CONJUNCT
46. of: Byron’s book of poems is a masterpiece.
- Adj. – WHAT KIND of book? Book of poems.
47. off: Jim took the soup off the stove.
- Adv. – WHERE did Jim take the soup? Off the stove?
- Location » Change of Location » Source: From what location?
48. on: We are cooking soup on the stove.
- Adv. – WHERE are we cooking soup? On the stove.
- Location: In what location?
49. onto: The cowboy hopped onto his horse.
- Adv. – WHERE did the cowboy hop? Onto his horse.
- Location » Change of Location » Goal: To what location?
50. opposite: We live in the house opposite the store.
- Adj. – WHICH house do we live in? The house opposite the store. (Uses location to specify which one.)
51. outside: We stood outside the store waiting for it to open.
- Adv. – WHERE did we stand? Outside the store.
- Location: In what location?
52. over: The flock of birds flew over the stadium towards the park.
- Adv. – WHERE did the flock of birds fly? Over the stadium.
- Location » Change of Location » Path: Along what path?
53. past: The kids walked past the candy store to the library.
- Adv. – WHERE did the kids walk? Past the candy store.
- Location » Change of Location » Path: Along what path?
54. pending: Lance was nervous pending his parent’s decision.
- Adv. – WHEN was Lance nervous? Pending his parent’s decision.
- Time » Time Period or Duration: What time period?
- Also related to Reason: Why?
- OR Adv. – DISJUNCT/ADJUNCT
55. per: Carl’s wage per hour is ten dollars.
- Adj. – WHAT KIND of wage? Per hour.
56. regarding: Jan’s ideas regarding the war are interesting.
- Adj. – WHICH IDEAS are interesting? Ideas regarding the war. (Specifies or limits which ones.)
57. sans: Hamilton ordered steamed vegetables sans broccoli.
- Adj. – WHAT KIND of vegetables? Vegetables sans broccoli.
58. since: Since my vacation, I have been very relaxed.
- Adv. – WHEN have you been relaxed since? Since my vacation.
- Time » Start Time/Origin in Time » Since when?
- Also related to Reason: Why?
- OR Adv. – DISJUNCT/ADJUNCT
59. than: Bruce is taller than me.
- Adverbial Complement – TEST: WHO is Bruce taller THAN? Me.
- DO-SO TEST: Bruce is taller than me, and Tim is so than Bruce. FAILED!
60. through: We drove through the tunnel.
- Adv. – WHERE did we drive? Through the tunnel.
- Location » Change of Location » Path: Along what path?
61. throughout: I have been lucky throughout my life.
- Adv. – WHEN have I been lucky? Throughout my life.
- Time » Time Period or Duration: What time period?
62. to: We went to a nice restaurant.
- Verb Complement – TEST: WHAT did we go TO? A nice restaurant.
- Location » Change of Location » Goal: To what location?
- DO-SO TEST: We went to a nice restaurant, and they did so to a bad restaurant. FAILED!
63. toward/towards: The river flows toward(s) the ocean.
- Adv. – WHERE does the river flow? Towards the ocean.
- Location » Direction of Motion: In what direction?
64. under: My cat sleeps under my bed.
- Adv. – WHERE does my cat sleep? Under my bed.
- Location » In what location?
65. underneath: The pipes underneath the building burst.
- Adj. – WHICH pipes burst? The pipes underneath the building. (Uses location to specify which one.)
66. unlike: Unlike the science test, the math test was easy.
- Adv. – DISJUNCT/CONJUNCT: Resemblance
67. until: Laura must wait until Tuesday.
- Adv. – HOW LONG must Laura wait? Until Tuesday.
- Time » Duration » End Point: Until when?
68. up: The trail up the mountain is treacherous.
- Adj. – WHICH trail is treacherous? The trail up the mountain.
69. upon: The crowd cheered upon the hero’s return.
- Adv. – WHEN did the crowd cheer? Upon the hero’s return.
- Time » Position in Time: At what time?
70. versus: The Lions versus the Hornets was a great game.
- Adj. – Modifies Lions. (specifies/limits)
71. via: We traveled to Italy via France. (through France)
- Adv. – WHERE did we travel? Via France (through France).
- Location » Change of Location » Path: Along what path?
72. with: The girl with the red hair sings beautifully.
- Adj. – WHICH girl sings beautifully? The girl with the red hair. (Uses description to specify which one.)
73. within: Jim lives within the city limits.
- Adv. – WHERE does Jim live? Within the city limits.
- Location » In what location?
74. without: The people without tickets had to leave.
- Adj. – WHICH people had to leave? The people without tickets. (Uses division [particularize] to specify which ones.)
Ten Concepts to Focus on When Analyzing These Examples
As you examine the examples, you will certainly learn a great deal about prepositions and prepositional phrases. But keep in mind, most prepositional phrases function as adjectives and adverbs; therefore, when you examine how prepositional phrases function in sentences, you also learn a great deal about how adjectives and adverbs function in sentences. In other words, there’s a lot to think about when you learn about prepositions and prepositional phrases.
Here are TEN fascinating categories to think about as you examine the sentences:
1. The Prepositions: All the prepositions are one-word prepositions; therefore, in all of the examples, the preposition will be the first word (and only the first word) of the prepositional phrase.
2. The Object of the Preposition: In all the examples, the object of the preposition will be the last word (and only the last word) of the prepositional phrase.
3. The Words Between the Preposition and the Object of the Preposition: All the words between the the preposition and the object of the preposition are functioning as adjectives. (Modern grammar classifies many of these adjectives as determiners.) These so-called adjectives include articles, possessives, numbers, participles, nouns as adjectives, and true adjectives. Note: It’s quite easy to add additional adjectives between the preposition and the object of the preposition.
4. The Word or Words that the Prepositional Phrase Modifies: Most of the following prepositional phrases modify verbs (adverbial) and a number modify nouns and pronouns (adjectival). Some of the prepositional phrases are sentence adverbs, which means they modify the entire sentence. A few of the prepositional phrases are verb complements, which means they complete the meaning of the verb.
5. The Questions that Adverbs Answer: When? How? Why? Where? To what extent? (To what extent? = How far? How long? How much? How often?)
6. The Questions that Adjectives Answer: Which ones? What kind?
7. The Categories of Adverbs: Location (position in space, direction, change of location, goal, source), Time (position in time, duration, frequency, relative time), Process (manner, means, instrument), Degree (distance, duration, frequency, scale) Cause and Result (reason, cause, purpose, concession, condition, result), Addition, Restriction.
8. Sentence Adverbs – Conjuncts and Disjuncts: These prepositional phrases don’t answer any of the traditional adverb questions, and therefore, they don’t modify just the verb. However, at some point in time, someone decided that these are adverbials, and that they modify the entire sentence. Conjuncts are TRANSITIONS and connect to what came prior; disjuncts look quite similar to conjuncts but are focused in on the sentence they are a part of.
9. Complements: We typically think of complements as predicate adjectives and predicate nominatives. Well, we also have adverbial complements. It’s often difficult to distinguish between prepositional phrases that are adverbial complements and adverbials. The Do-So Test is the best test for determining whether the prepositional phrase is an adverbial or a complement.
10. Location in the Sentence and Movability: Are the prepositional phrases located at the beginning, middle, or end of the sentence? Can the prepositional phrase be moved to a different location in the sentence? Adjectival prepositional phrases are not movable. Adverbial prepositional phrases are usually movable, but with one position likely to be more effective than the other positions.
A Note to Teachers: Common Prepositions vs. Uncommon Prepositions
Students repeatedly learn the same common prepositions year after year. And it’s for this reason that students fail to correctly understand prepositions and prepositional phrases. By examining at least a few of the less common prepositions in action, you will better understand prepositions and prepositional phrases. Furthermore, you will likely see a number of words that you didn’t realize can be used as prepositions.
I had two goals with this page:
1. I wanted to keep the examples simple and short so the relationships and analysis are made clear.
2. I wanted to use every single widely-accepted simple (one-word) preposition in an example sentence. Other one-word prepositions do exist, but most are rare, archaic, debatable, or will lead to confusion.
Even with a desire to keep things clear and simple, in the process of creating these examples, I found myself dealing with advanced concepts such as complements, participle prepositions, and sentence adverbs (disjuncts and conjuncts). You will find examples of all these advanced concepts in the examples for one very important reason: They could not be avoided. The fact is that even simple prepositions in simple prepositional phrases in simple sentences can involve complicated concepts. In short, we don’t need a complicated sentence for a complicated concept to exist.